Introduction
When it comes to earthy substances with remarkable properties, Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite are at the forefront. These materials are sought after for their unique characteristics and versatile applications. In this article, we will break down the distinctions between Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite, helping you make informed decisions in various fields, from agriculture to environmental conservation.
What is Bentonite?
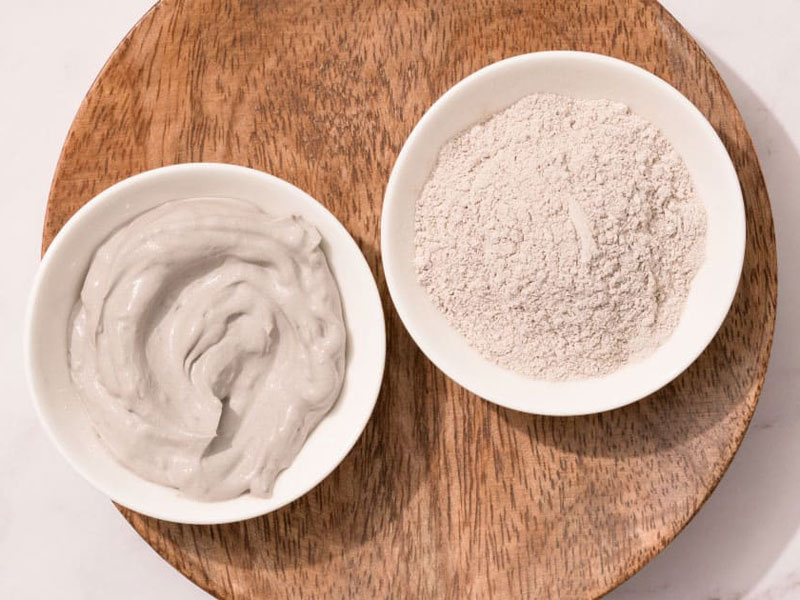
Bentonite, a versatile natural clay, derives its name from Fort Benton, Wyoming, where it was first identified. It is a hydrous aluminum phyllosilicate, composed mainly of montmorillonite. This unique clay has remarkable water-absorbing properties, making it a valuable resource in various industries.
The Formation of Bentonite
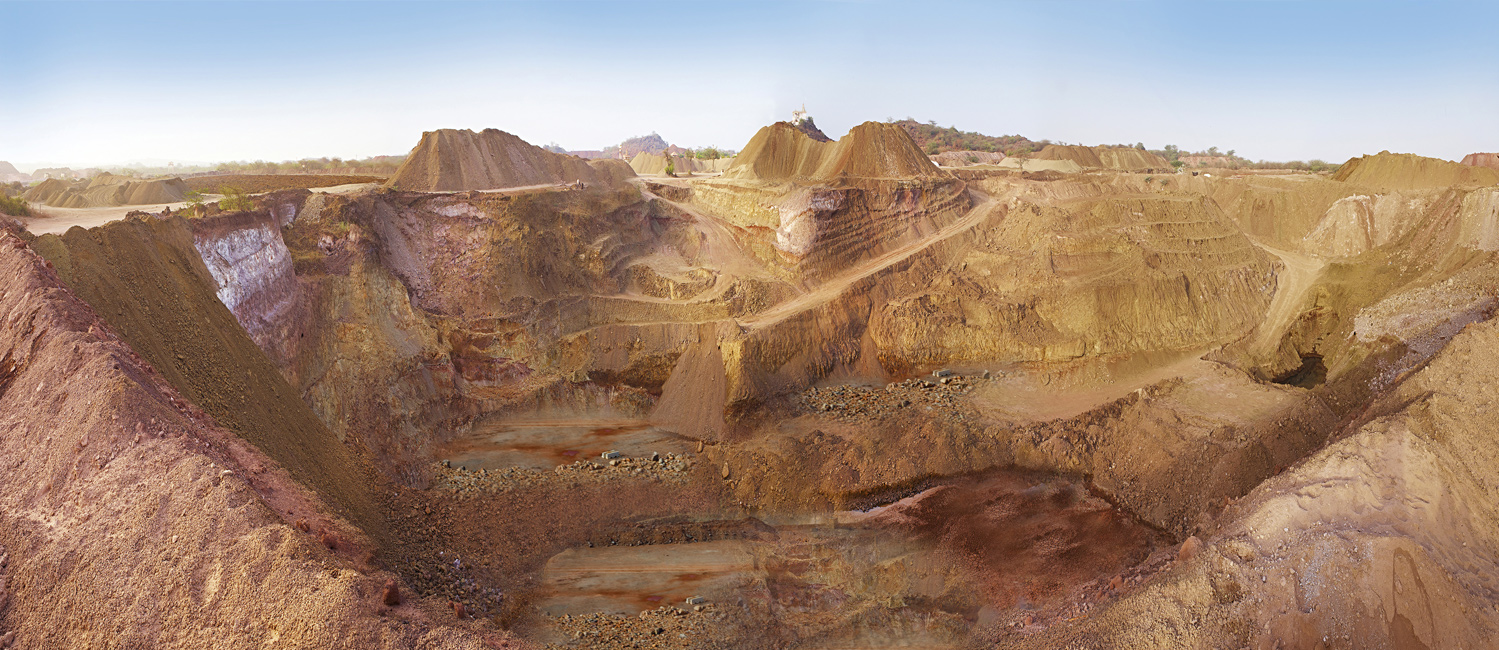
Bentonite primarily forms from volcanic ash and is deposited in marine environments. Over millions of years, the minerals in the ash undergo chemical alterations, resulting in the formation of Bentonite clay. Its properties are heavily influenced by the specific minerals present in the volcanic ash, as well as the environmental conditions during its formation.
Types of Bentonite
Sodium Bent onite
Sodium Bentonite is a specific type of Bentonite clay that is highly valued for its exceptional swelling capacity. It contains a high percentage of sodium ions in its structure, which makes it an excellent sealant in various applications. Sodium Bentonite is known for its ability to absorb water and expand significantly, creating an impermeable barrier.
Calcium Bentonite
Calcium Bentonite, on the other hand, has a higher calcium ion content. While it also exhibits swelling properties, it is not as effective as Sodium Bentonite in sealing applications. Calcium Bentonite is often used in health and wellness products due to its potential detoxifying properties.
Potassium Bentonite
Potassium Bentonite contains a significant amount of potassium ions and is less common than Sodium and Calcium Bentonite. It has unique properties that make it suitable for specialized industrial applications.
Read More: Wikipedia
Sodium Bentonite: A Closer Look
Sodium Bentonite Properties
Sodium Bentonite’s exceptional ability to swell upon contact with water is a result of its high sodium ion content. When hydrated, the clay particles expand, creating a tight seal that is impermeable to liquids. This property makes Sodium Bentonite a popular choice for applications where water and fluid containment are crucial.
Bentonite vs. Sodium Bentonite
Differences in Composition
The key difference between Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite lies in their chemical composition. While Bentonite is a broad term that encompasses various clay types, Sodium Bentonite is a specific subtype characterized by its high sodium ion content. This difference in composition directly impacts their properties and applications.
Swelling Capacity
One of the most significant distinctions between Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite is their swelling capacity. Sodium Bentonite can absorb water and expand up to several times its original volume, creating a tight, impermeable seal. This property makes it ideal for sealing ponds, landfills, and preventing water leakage in construction projects.
Industrial Applications
Both Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite find applications in various industries, but Sodium Bentonite’s superior swelling capacity makes it the preferred choice for applications where water sealing is essential. Some common applications include:
- Pond and lake sealing
- Landfill liners
- Drilling mud in oil and gas exploration
- Environmental remediation
- Geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs)
- Foundry industry
Read More: Kalolin
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability of Bentonite
Bentonite, in general, is considered an environmentally friendly material due to its natural origin and non-toxic properties. It is often used in environmental conservation projects, such as sealing landfills to prevent groundwater contamination.
Pros and Cons of Bentonite
Pros:
- Natural and abundant resource
- Versatile applications in various industries
- Effective in sealing and containment applications
Cons:
- Swelling capacity not as high as Sodium Bentonite
- Limited use in applications requiring high water absorption
Pros and Cons of Sodium Bentonite
Pros:
- Exceptional swelling capacity
- Highly effective in water sealing applications
- Versatile in a wide range of industries
Cons:
- Relatively more expensive than other clay types
- Limited effectiveness in applications not requiring swelling capacity
Choosing the Right Type for Your Needs
Selecting between Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite depends on the specific requirements of your project. If you need a reliable water sealant, Sodium Bentonite is the go-to choice. For other applications where swelling capacity is not critical, regular Bentonite may suffice.
Read More: Drilling Barite
Conclusion
In the world of clay materials, Bentonite and Sodium Bentonite stand out as versatile substances with unique properties. While Bentonite encompasses various clay types, Sodium Bentonite shines with its remarkable swelling capacity, making it a preferred choice for water sealing applications. Understanding the differences and advantages of these clays can help you make informed decisions in agriculture, construction, and environmental conservation.